
Alexis started the month with stock that had a cost of $8,300, which is her beginning inventory. Over the month, she ordered materials to make new items and ordered some products to resale, spending $4,000, which are her inventory costs. At the end of the month, she calculated that she still had $5,600 in stock, which is her ending inventory. Cost of goods sold does not include costs unrelated to making or purchasing products for sale or resale or providing services. General business expenses, such as marketing, are often incurred regardless of if you sell certain products and are commonly classified as overhead costs.
Contextualize COGS with your gross profit margin.
- Very briefly, there are four main valuation methods for inventory and cost of goods sold.
- Buying the inventory you’ll eventually sell is an inevitable cost of running your business, but smart COGS management makes a difference.
- COGS is the cost incurred in manufacturing the products or rendering services.
- Gross profit also helps to determine Gross Profit Margin, a percentage that indicates the financial health of your business.
- By subtracting what inventory was leftover at the end of the period, you calculate the total cost of the goods you sold of that available inventory.
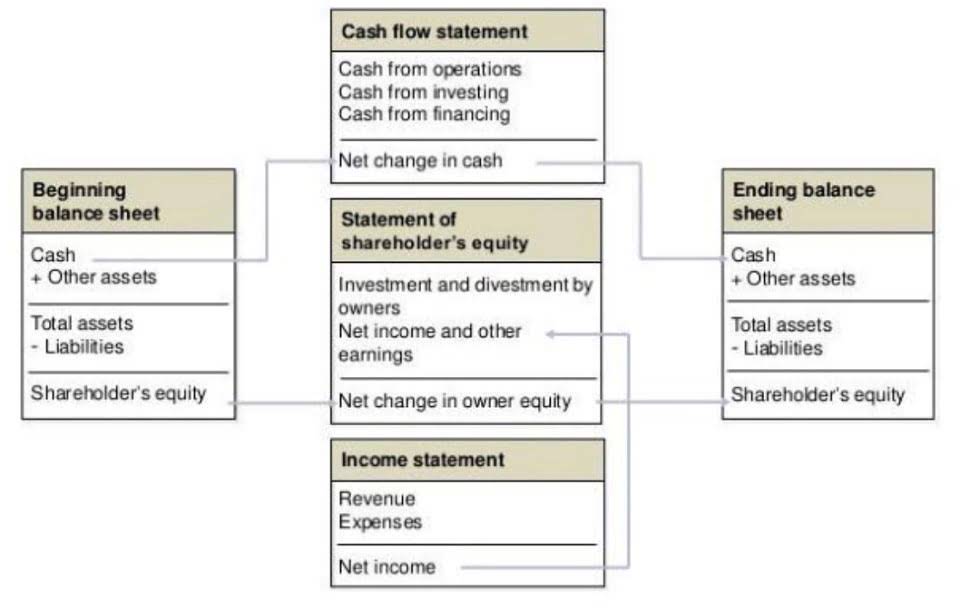
Operating expenses help establish a budget for each department and evaluate the overhead costs spent by the company. Operating expenses include utilities, rent, office supplies, sales and marketing, legal costs, insurance, and payroll. Operating expenses are expenses that are indirectly tied to producing the goods or services. There are four methods that a company can use when recording its inventory sold during a period. The IRS has set specific rules for which type of method a company can use and when to make changes to the inventory cost method. To get more info on how to build your own report, check out our page on how to prepare an income statement.
Are salaries included in COGS?

Cost of goods is the cost of any items bought or made over the course of the year. Once you have gathered the relevant information, you cost of goods sold can calculate the cost of goods sold. This is because such service-oriented businesses do not have any Cost of Goods Sold (COGS).
Cost of Goods Sold Formula for Manufacturers
- FIFO and specific identification track a single item from start to finish.
- Typically this would be a month, or a quarter, or a year, but it could be any period you choose.
- Higher COGS with disproportionate pricing can leave your business in a deficit position if the prices are too low or alienate consumers if the price is too high.
- Some software can even help you decide on an inventory accounting method by showing which is most advantageous for you.
Variable costs are costs that change from one time period to another, often changing in tandem with sales. To calculate it, add the beginning inventory value to the additional inventory cost and subtract the ending inventory value. There are also some cases that businesses, specifically service companies, do not have COGS and inventories, thus, no COGS are displayed on their respective income statements.
While COGS focuses, obviously, on cost, the metric is calculated in a roundabout way. In other words, the formula focuses on the time frame rather than expenses. The COGS definition state that only inventory sold in the current period should be included. It doesn’t, however, state what order inventory is deemed to be sold.

How do you calculate the variable cost of goods sold?
A standard accounting module helps keep tabs on the books while seamless integrations with respected financials software like QuickBooks and Xero make sure all finances are always under control. One of the primary purposes of tracking COGS is so that you can write it off on your taxes. Each time you incur an expense related to inventory, create a journal entry on your books with the correct expense category. When you pull a profit and loss (P&L) sheet, your COGS will appear on the income statement underneath sales. Let’s say the same jeweler makes 10 gold rings in a month and estimates the cost of goods sold using LIFO.
What items are included in COGS?
- So, if we consider companies providing services to their clients, such companies neither have goods to sell nor have any inventories.
- Such cost would include costs like cost of material, labour, etc. however, it does not consider indirect costs such as salaries for determining the Cost of Revenue.
- Thus, in this case, cost is attached to each withdrawal or sale of items.
- With the exception of Specific Identification, all of the abovementioned methods provide cost estimations for sold inventory.
- During times of inflation, FIFO tends to increase net income over time by lowering the COGS.
- The cost of goods sold applies only to businesses that sell products.
The average cost method uses a basic average of all similar items in the inventory, regardless of purchase date. Calculating your cost of goods sold tells you how much it costs to create a product—so if you know your COGS, you know what price to sell your goods at to turn a profit. The basic purpose of finding COGS is to calculate the “true cost” of merchandise sold in the period.
Knowing your initial costs and maintaining accurate product costs can ultimately save you money. Some service companies may record the cost of goods sold as related to their services. But other service companies—sometimes known as pure service companies—will not record COGS at all. The difference is some service companies do not have any goods to sell, nor do they have inventory. There are other inventory costing factors that may influence your overall COGS. The IRS refers to these methods as “first in, first out” (FIFO), “last in, first out” (LIFO), and average cost.
How to Calculate Cost of Goods Sold in Your Business
A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation. We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed resources. While this may entail a higher initial investment, it can pay off in the long run by reducing your overall costs.
Compare the best bookkeeping software for small businesses
The LIFO method assumes higher cost items (items made last) sell first. Thus, the business’s cost of goods sold calculation will be higher because the products cost more to make. LIFO also assumes a lower profit margin on sold items and a lower net income for inventory.

